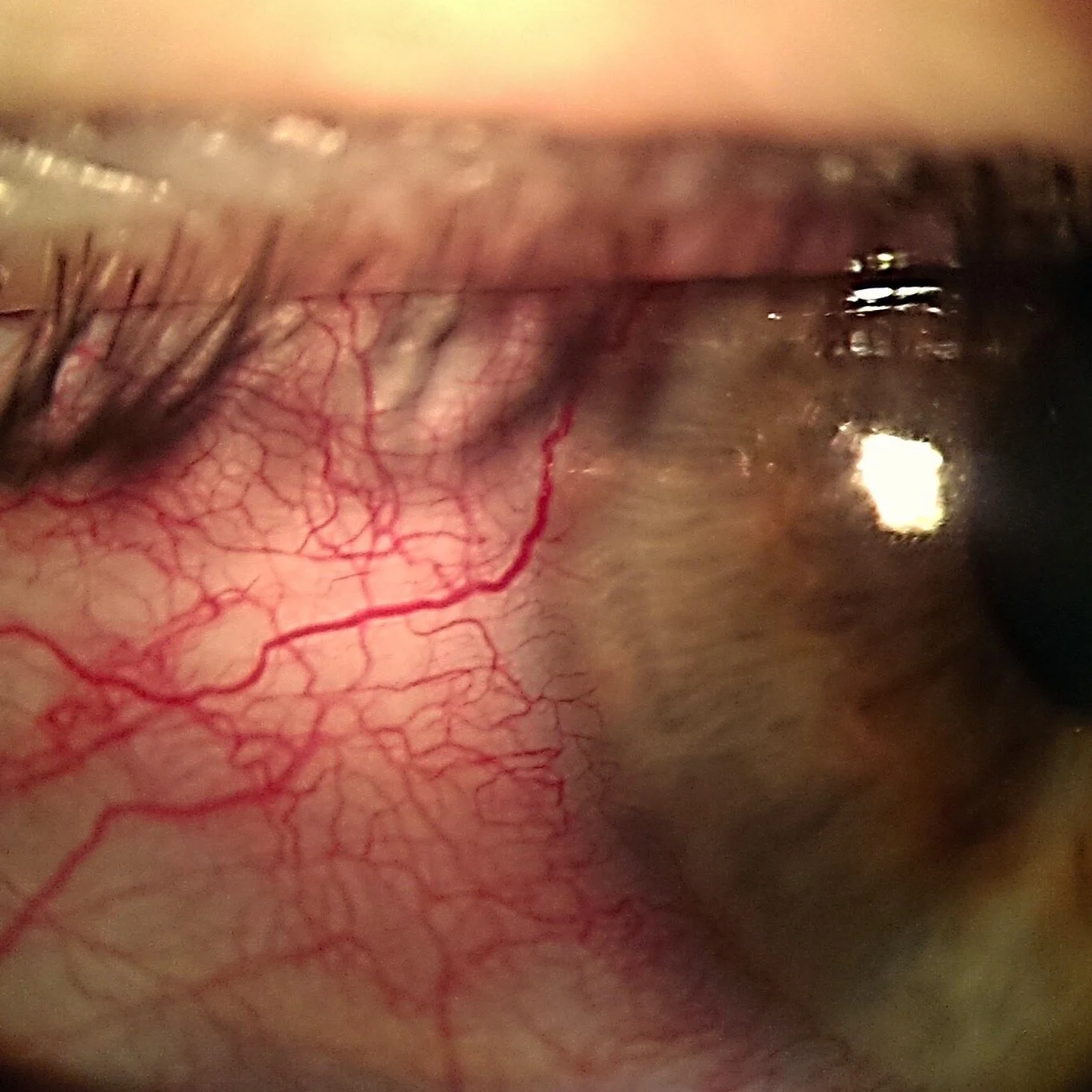
Keratitis
Keratitis is a serious condition involving inflammation or infection of the cornea, the clear front part of your eye. If left untreated, it can pose a significant risk to your vision. However, with prompt and appropriate treatment, keratitis can be resolved without long-term complications. It’s crucial to see an optometrist or ophthalmologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Keratitis
Keratitis can occur in several forms, each with different causes:
Infective Keratitis: Caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
Allergic Keratitis: Associated with allergic reactions, such as atopic keratoconjunctivitis or vernal keratoconjunctivitis.
Contact Lens-Associated Keratitis: Often linked to improper contact lens use or hygiene.
Toxic Keratitis: Caused by exposure to harmful chemicals or substances.
Signs & Symptoms
The symptoms of keratitis can vary widely, but some key signs to watch for include:
Redness of the eye
Pain, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Blurred or reduced vision
Discharge from the eye
You may not experience all of these symptoms, but if you notice any, it's important to seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment
If you experience symptoms of keratitis, it’s essential to visit your optometrist or eye specialist immediately. The treatment will depend on the specific cause of your keratitis:
Prescription Eye Drops: Often used to treat bacterial or viral infections.
Oral Medication: May be necessary for more severe infections.
Hospital Referral: In severe cases, especially when vision is at risk, you may need to be referred to a hospital for advanced treatment.
Key Points to Remember
Keratitis is a potentially serious condition that can lead to vision loss if not treated promptly.
Symptoms include redness, pain, light sensitivity, and blurred vision.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes.